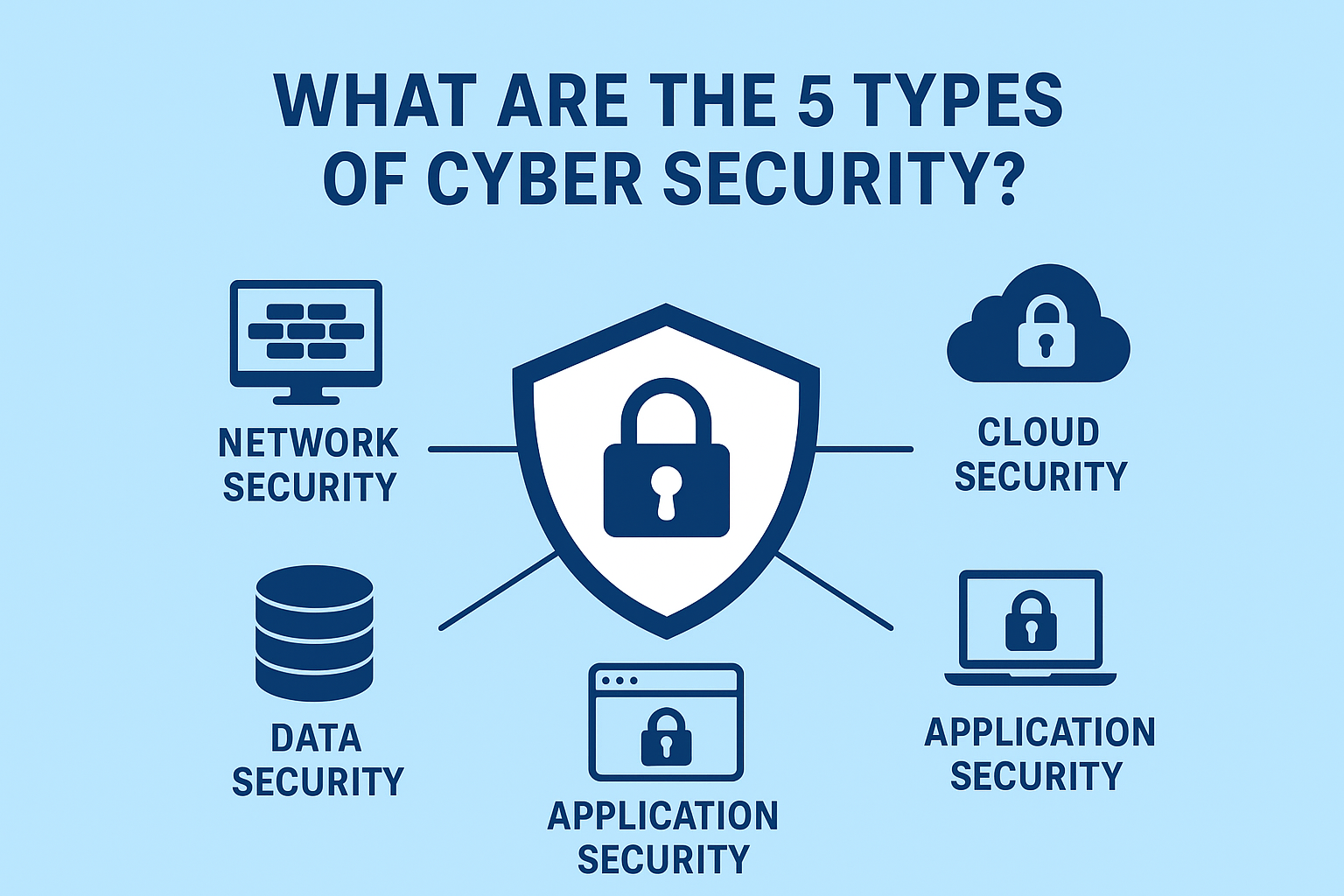
Cyber security has become a core necessity for every modern business, regardless of size or industry. With cyberattacks growing more frequent and sophisticated, organisations must understand what are the five types of cyber security and how each layer plays a vital role in protecting systems, data, and digital assets. Implementing these layers not only strengthens digital defences but also enhances business continuity, customer trust, and long-term resilience. This detailed guide explains the five major types of cyber security, the benefits of cyber security for businesses, and essential best practices including why network security is important, cloud security best practices, endpoint protection for companies, application security measures, how to secure business data online, and proven data security strategies. It also covers the growing importance of cyber security monitoring services and managed cyber security services for businesses seeking expert protection.
1. Network Security
Network security is the foundation of a secure IT environment and one of the most critical layers of defence. It focuses on safeguarding an organisation’s interconnected systems, devices, and communication channels from unauthorised access, malware, data breaches, and misuse. Understanding why network security is important is essential for preventing attackers from infiltrating your infrastructure. Strong network security protects both internal and external communication, reduces vulnerabilities, and prevents ransomware, phishing, and DDoS attacks from spreading across the organisation. Businesses rely on tools such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), secure Wi-Fi configurations, segmentation, and Zero Trust models to enforce strict access controls. These measures ensure that every device, user, and data packet is verified and monitored, reducing the risk of cyber threats moving laterally within the network.
2. Cloud Security
Cloud security has become increasingly important as businesses shift their operations to platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft 365. Cloud environments store sensitive data, host applications, and manage essential business processes, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Implementing strong cloud security best practices ensures that cloud-stored assets remain protected against unauthorised access, misconfigurations, and breaches. Best practices include enabling multi-factor authentication, encrypting data at rest and in transit, enforcing least-privilege access control, monitoring cloud activity logs, and ensuring compliance with standards like GDPR and ISO 27001. Cloud security also involves regular vulnerability assessments to detect gaps before attackers can exploit them. Businesses that take cloud protection seriously enjoy improved scalability, security automation, and reliable disaster recovery.
3. Endpoint Security
Endpoint security protects individual devices such as laptops, servers, smartphones, and IoT devices connected to a business network. As remote and hybrid work environments expand, strong endpoint protection for companies has become critical. Endpoints are common entry points for malware, phishing, ransomware, and credential theft. Effective endpoint security includes advanced antivirus tools, mobile device management (MDM), patching outdated software, and implementing Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions that provide real-time visibility and rapid threat remediation. Modern endpoint security also focuses on behavioural analysis, which identifies suspicious activities even if they do not match known malware signatures. Companies that prioritise endpoint protection significantly reduce the risk of internal breaches, data leakage, and compromised user accounts.
4. Application Security
Application security ensures that the software businesses use—including websites, mobile apps, and internal applications—remains safe from malicious attacks. Hackers frequently exploit flaws in application code to gain entry into business systems. Implementing strong application security measures prevents attacks such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and session hijacking. Effective measures include secure coding practices, automated code scanning, penetration testing, patch management, encryption of sensitive fields, and the use of Web Application Firewalls (WAFs). These techniques help ensure that applications remain resilient against both internal errors and external threats. With more businesses adopting digital platforms, application security is essential to prevent service disruptions, protect customer data, and maintain operational integrity.
5. Data Security
Data security protects sensitive business information from theft, manipulation, or unauthorised access. As cyberattacks increasingly target personal data, financial records, and intellectual property, companies must adopt strong data security strategies to keep information safe. Essential strategies include encryption, data classification, strict access control, secure backups, and Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools. Data security also involves regular audits to ensure compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR. Companies that prioritise data protection build customer trust, reduce legal risks, and maintain smooth business operations even during cyber incidents. Strong data security strategies ensure that even if attackers penetrate other layers, sensitive information remains inaccessible.
Benefits of Cyber Security for Businesses
Implementing robust cyber security delivers numerous benefits for organisations. First, it significantly reduces the risk of data breaches, ransomware, and financial losses. Businesses protect customer information, maintain trust, and avoid costly downtime caused by attacks. Strong cyber security practices also ensure regulatory compliance, preventing penalties and legal issues. Investing in cyber security enhances long-term business growth by improving operational reliability, enabling safe digital transformation, and defending intellectual property. Businesses also gain competitive advantages by demonstrating their commitment to secure operations. When combined with cyber security monitoring services and managed cyber security services, companies ensure round-the-clock protection and expert oversight that internal teams may not be able to provide.
How to Secure Business Data Online
Protecting business data online is a continuous process requiring strong policies, employee awareness, and layered protection. Key steps include using strong passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication, implementing encryption, and controlling user access to sensitive information. Training employees to detect phishing attempts is essential, as human error causes many data breaches. Regular backups and secure cloud storage help businesses recover quickly during cyber incidents. Monitoring user activity, updating software, and enforcing least-privilege permissions further strengthen online data protection. Following these methods ensures businesses understand how to secure business data online and maintain control over their digital assets.
Cyber Security Monitoring Services
Modern cyber threats are persistent and rapidly evolving, which makes continuous monitoring essential for detecting suspicious activities before they escalate. Cyber security monitoring services provide 24/7 surveillance of networks, endpoints, cloud environments, and logs. These services use advanced tools such as SIEM, AI-driven analytics, threat intelligence, and automated alerts to detect potential breaches early. Continuous monitoring ensures that security teams respond instantly to risks, reducing the damage of ransomware, malware infections, insider threats, or unusual login behaviour. Monitoring services are vital for businesses without in-house security teams, offering proactive threat detection instead of reactive response.
Managed Cyber Security Services
Many businesses lack the expertise, tools, or time to manage cyber security internally. Managed cyber security services provide professional support by outsourcing security to experts who handle monitoring, threat detection, incident response, compliance, and overall security management. These services include vulnerability assessments, patching, endpoint management, disaster recovery planning, and security consulting. By partnering with a managed security provider, businesses benefit from enterprise-level protection at a lower cost. Managed services ensure that all five types of cyber security are continuously maintained, updated, and optimised, allowing businesses to focus on their core operations while staying protected from evolving threats.
Conclusion
Understanding what are the five types of cyber security is essential for protecting business systems, networks, applications, and data. With cyberattacks on the rise, businesses must implement strong security layers covering network, cloud, endpoints, applications, and data protection. The benefits of cyber security for businesses are extensive, from reducing risks to ensuring compliance and maintaining customer trust. By adopting cloud security best practices, investing in endpoint protection for companies, enforcing strong application security measures, and applying proven data security strategies, organisations can defend against complex cyber threats. For ongoing protection, cyber security monitoring services and managed cyber security services provide expert support and continuous vigilance. Businesses that prioritise security today ensure a safer, more resilient digital future tomorrow.
FAQs
Q1. What are the five types of cyber security?
Network security, cloud security, endpoint security, application security, and data security.
Q2. What are the 7 types of cyber security with examples?
-
Cloud Security – MFA in cloud apps
-
Endpoint Security – Antivirus on devices
-
Application Security – Web Application Firewall (WAF)
-
Data Security – Encryption
-
Identity & Access Management (IAM) – Role-based access
-
Operational Security (OpSec) – Secure backup policies
Q3. What are the five types of computer security?
Physical security, network security, information security, operational security, and application security.
For more learning stay tunned with TECHWORLD