In today’s fast-changing technology environment, terms like artificial intelligence and machine learning are often used as if they mean the same thing, but they are distinct concepts. Knowing the difference is essential for professionals, students, and organizations aiming to use these technologies effectively. In this guide, you will learn how machine learning differs from broader intelligent systems with real-world examples, explore the various types of intelligent technologies and learning algorithms, understand the distinction between machine learning and generative learning models, and access practical resources such as free guides and beginner-friendly courses to gain hands-on experience.
Definition: What Distinguishes Machine Learning from Artificial Intelligence
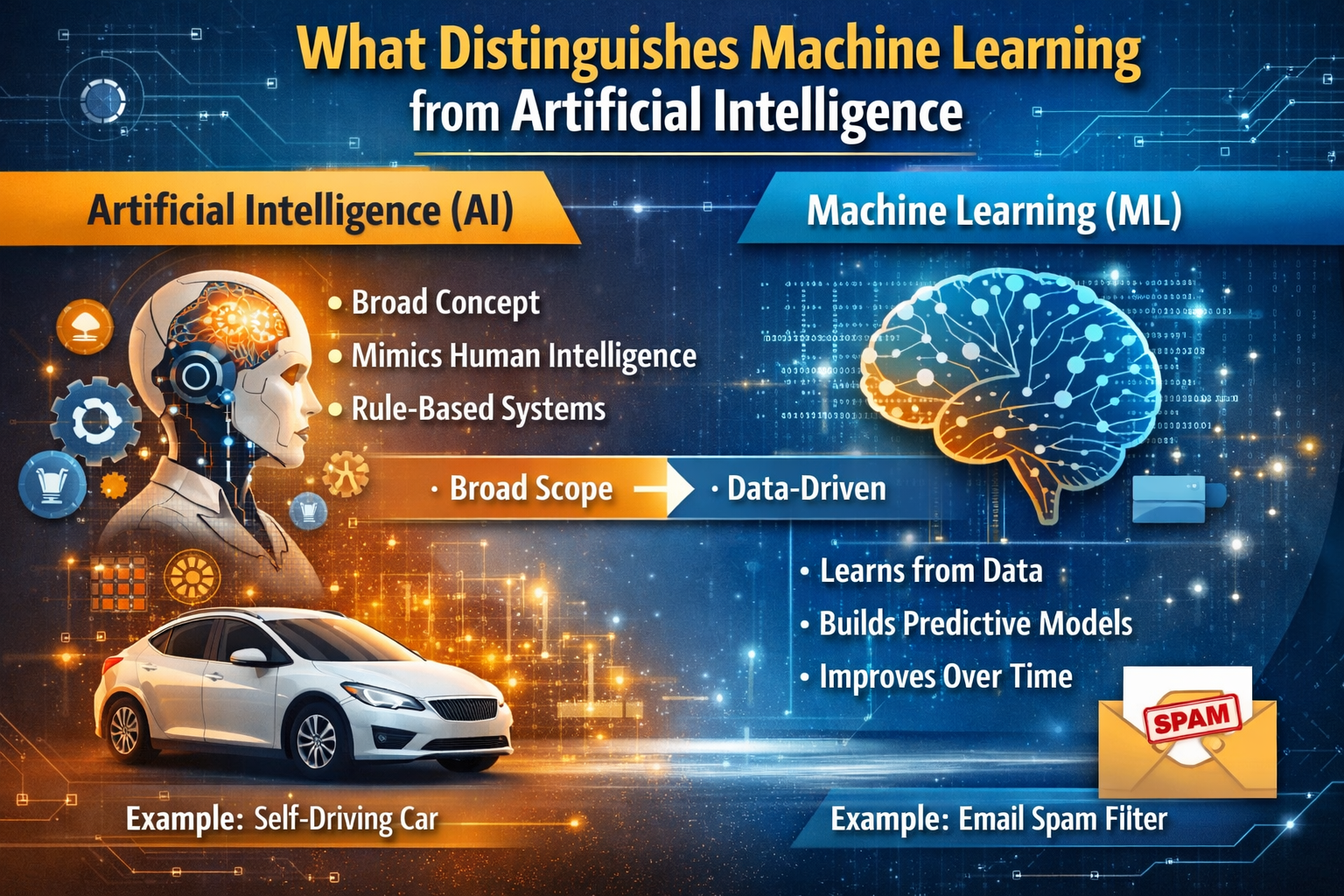
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the broader concept of machines performing tasks in ways that mimic human intelligence. These tasks can include problem-solving, decision-making, language understanding, or perception. AI is the umbrella technology encompassing various subfields, including machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), robotics, computer vision, and expert systems.
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI focused on creating systems that learn from data without being explicitly programmed. In ML, algorithms identify patterns and improve their performance over time based on experience. Examples include recommendation engines (like Netflix suggestions), email spam filters, and fraud detection systems used by banks.
Key Distinction:
-
AI is the goal — creating intelligent machines.
-
ML is the method — a way to achieve that goal by training machines with data.
Why Understanding the Difference Matters
Knowing the difference between AI and ML is not just academic. It influences:
-
Career decisions: Understanding which skill sets to develop.
-
Business strategy: Selecting the right technologies for automation, analytics, or product development.
-
Project planning: Determining whether a system needs rule-based AI logic or data-driven learning.
For example, companies like Google DeepMind, OpenAI, and Microsoft AI focus heavily on ML models to drive intelligent applications like ChatGPT or image recognition systems. Mislabeling AI and ML can lead to misunderstandings in technical discussions or project requirements.
Key Concepts and Components
Understanding types of artificial intelligence and machine learning is essential:
Types of AI
-
Narrow AI (Weak AI): Performs specific tasks, e.g., voice assistants like Siri or Alexa.
-
General AI (Strong AI): Hypothetical AI capable of reasoning across multiple domains (not yet realized).
-
Superintelligent AI: Advanced theoretical AI exceeding human intelligence.
Types of Machine Learning
-
Supervised Learning: Learns from labeled data. Example: email spam detection.
-
Unsupervised Learning: Finds patterns in unlabeled data. Example: customer segmentation.
-
Reinforcement Learning: Learns through trial and error. Example: self-driving car navigation.
-
Generative AI: Creates new data from learned patterns, e.g., ChatGPT, DALL·E, or MidJourney.
Machine Learning vs Generative AI Explained
While ML focuses on pattern recognition and prediction, generative AI is a specific type of ML that creates entirely new content. Examples include:
-
Text generation: ChatGPT producing human-like answers.
-
Image generation: DALL·E or Stable Diffusion creating realistic visuals.
-
Audio synthesis: Tools generating music or voice content.
Generative AI models rely on ML algorithms trained on massive datasets, making them a practical application of ML rather than a separate field.
Benefits and Real-World Use Cases
AI and ML power numerous industries and applications:
-
Healthcare: Predicting diseases, analyzing medical images, automating clinical documentation.
-
Finance: Fraud detection, credit scoring, algorithmic trading.
-
Retail: Personalized product recommendations and inventory forecasting.
-
Transportation: Autonomous vehicles and route optimization.
-
Customer Service: AI chatbots and virtual assistants handling support queries.
For beginners, free AI and machine learning PDF guides and beginner-friendly AI and machine learning courses are available from platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy, providing hands-on exercises and real-world examples.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
-
“All machine learning is AI” — Not all ML applications are considered AI if they perform narrow, rule-based tasks.
-
Confusing generative AI with traditional ML — Generative AI creates new content, while traditional ML predicts or classifies.
-
Thinking AI replaces humans — Most AI systems augment human intelligence rather than fully replace it.
Best Practices and Tips
-
Start with supervised and unsupervised ML projects to build foundational skills.
-
Explore open datasets for hands-on practice (e.g., Kaggle, UCI Machine Learning Repository).
-
Combine ML knowledge with cloud platforms like AWS SageMaker, Google Cloud AI, or Microsoft Azure ML for real-world deployment.
-
Keep updated with AI research papers and technology updates from OpenAI, DeepMind, or NVIDIA.
Relevant Examples
-
Netflix Recommendations: ML predicts which shows you may like based on past behavior.
-
Healthcare Diagnostics: AI models analyze X-rays to detect diseases earlier than human radiologists.
-
ChatGPT: Uses generative AI to create human-like text for customer service or content creation.
-
Autonomous Vehicles: Reinforcement learning and computer vision combine to navigate roads safely.
Conclusion
Distinguishing between Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) is important for professionals, students, and businesses trying to succeed in today’s technology-driven world. AI is the broader concept that focuses on creating machines capable of performing tasks that normally require human intelligence, while ML is a key part of AI that allows systems to learn from data and improve their performance over time. Understanding their types, differences, and real-world applications helps individuals make smarter decisions about career paths, project development, and business strategies. By exploring practical examples and using accessible resources—such as free AI and machine learning PDF guides or beginner-friendly courses—you can build strong knowledge and skills in this rapidly evolving and highly influential field.
Also read:
What Is the Best AI Stock to Buy Now in 2026? A Complete Investor Guide
FAQs
Q1.What distinguishes machine learning from AI?
AI is the broader concept of machines performing tasks that mimic human intelligence, while machine learning is a subset that enables machines to learn from data and improve over time.
Q2.What is the difference between AI and machine learning jobs?
AI jobs focus on designing intelligent systems, problem-solving, and overall strategy, whereas machine learning jobs specialize in building and training data-driven models for specific tasks.
Q3.Is AI possible without machine learning?
Yes, AI can exist without machine learning through rule-based systems, expert systems, and traditional algorithms, but it may be less flexible and adaptive.
Q4.What is a key difference between AI machines and regular machines?
AI machines can adapt, make decisions, and learn from experience, while regular machines follow predefined instructions without independent learning.